 Many of us are familiar with the terms “slipped disc” and “herniated disc.” But few people outside the medical profession truly understand how critical their spinal discs are. Without discs, our vertebrae would grind against each other and our spines would collapse under the strain.
Many of us are familiar with the terms “slipped disc” and “herniated disc.” But few people outside the medical profession truly understand how critical their spinal discs are. Without discs, our vertebrae would grind against each other and our spines would collapse under the strain.
A whole host of things can go wrong with a vertebral disc over a lifetime. A traumatic injury can crush or misplace a disc. An excessive pulling or lifting accident at home or on the job can force a disc out of position. And for some of us, simply getting older can cause a disc to deteriorate. This is usually called degenerative disc disease.
First, what exactly is a disc?
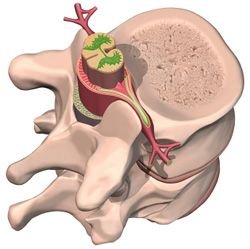
Vertebral discs are the shock absorbers that are found between vertebral bodies. Each disc is essentially sandwiched between two vertebrae supported by ligaments. Composed of collagen, discs have a tough outer core and a soft inner core. When you are born, these discs are mostly water. As you get older, the discs slowly lose their water content and get harder. As they dehydrate over time, your discs provide less of that soft and cushy support they provided when they were new. Because they have no blood supply and few nerve endings, discs are unable to repair themselves. Disc degeneration can be painful in later years; in some cases, the inner core of the discs leak proteins that can inflame the nerve roots.
Common disc disorders
Disc disorders are generally classified as contained discs or noncontained discs. Contained discs are discs that are essentially intact, but protruding where they do not belong. Noncontained discs are ruptured discs that also may protrude into another area of the spine, leaking their fluid and causing havoc.
A common contained disc disorder is a bulging disc. Bulging discs may push into the spinal canal. A common noncontained disc disorder is a herniated disc, which has ruptured, usually at its weakest point. The fluid inside herniated discs is an irritant to the delicate soft tissues of the spinal cord, none the least being the nerves. Nerves that have become exposed to this fluid often swell in response. In some cases, parts of a herniated disc’s tough outer shell can break off into the spinal canal, causing further irritation.
The vast majority of herniated discs occur in the lower back or lumbar region. When a lumbar herniated disc presses on a nerve root, it can cause radiating pain, numbness and weakness in other areas of the body, including the buttocks, leg, ankles and toes. Ironically, in many cases, a person with a herniated disc will not feel back or neck pain.
Cervical (neck) discs that have herniated can cause radiating pain and numbness down an arm and into the wrist and hand. Other types of symptoms include shoulder pain and numbness, as well as muscle and reflex weakness.

