 Whiplash is probably one of the most misunderstood and misaligned kinds of injuries; people involved in automobile accidents often suspect they have whiplash if they feel any kind of soreness in their neck. This is not to diminish the fact that whiplash is quite a common and potentially serious kind of injury incurred in automobile collisions.
Whiplash is probably one of the most misunderstood and misaligned kinds of injuries; people involved in automobile accidents often suspect they have whiplash if they feel any kind of soreness in their neck. This is not to diminish the fact that whiplash is quite a common and potentially serious kind of injury incurred in automobile collisions.
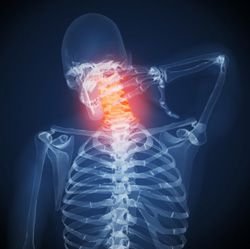
What is whiplash? Whiplash is an injury to the cervical spine, or neck, and occurs when the muscles and other soft tissues are hyperextended or hyperflexed.
Most instances of whiplash occur during a front-end or rear-end automobile collision. The force of the vehicle being struck or striking another object are quite powerful, and can cause the neck muscles, ligaments, and tendons to twist and turn with incredible, unnatural force. These tissues, which are stretched far beyond their natural limits, can become torn and, in some cases, permanently damaged. In addition, vertebral discs in the cervical spine can bulge, tear, and rupture.
Symptoms of whiplash may include one or more of the following:
- Blurred vision or dizziness
- Ear ringing
- General stiffness
- Headaches, especially behind the eyes
- Nausea
- Numbness, or burning, piercing and/or radiating pain in the neck, jaw, face, shoulders (and between the shoulder blades), and arms, which is usually a sign of a muscle or ligament tear.
- Pain in any of the extremities
- Sharp pains when moving an extremity, such as an arm or finger (a possible sign of disc damage).
- Swallowing difficulty
Many people who incur whiplash are treated with a device called a cervical collar, a soft cushion that envelopes the neck and keeps the weight of the head from applying undue pressure to damaged tissues during the healing process.

